I love the Cannes Lions Festival of Creativity.
There. I said it.
I’ll admit that I’ve had my moments of scepticism over the years, but we need Cannes – perhaps now more than ever.
We need it for the celebration of the work. For the ideas. To shape and focus the industry agenda. We need it to logistically get people in one place at one time. For the opportunities to reconnect with old colleagues and friends – and make some new ones. Because it reminds us of what we do when we’re at our collective best. We need it for all those reasons, and many more besides.
I used also to think that we needed Cannes to show us the future – but I don’t think that’s the case anymore. Because the future has arrived already. We are living inside it.
My take on the vibe at Cannes Lions 2025 was of an industry not bracing for a future to come, but rather one wrestling with the reality of its arrival. It was a thought that dawned on me Tuesday whilst I was talking with a long-time industry acquaintance; that the future has moved from being something rushing towards us – into something that now lies behind us. It simply moved faster than our ability to keep pace with the changes it wrought. And now we’re playing catch up.
And so here we were. Navigating together the shared reality of our transformed world.
There was no better example of this new reality than YouTube’s presentation in the Palais des Festivals cavernous Lumiere Theatre. Less a presentation than a victory lap, the streaming platform’s CEO Neal Mohan shared with the audience that a billion hours of YT are watched daily on television sets – YouTube is the new TV. With Kaizen – the story of Inoxtag’s Everest climb – he suggested that YouTube creators are also now the new Hollywood start-ups.
Alongside creator content’s expanding influence over the industry is the halo of fan content that accompanies it – often in podcast form. Mohan shared that 1bn people watch a podcast every month on YouTube, noting the power of the connection between creators and fans – observing that “fans don’t follow culture, they shape it … fandom itself is a form of creative expression”.
Brands need not miss out on the action. Chicken Shop Date’s Amelia Dimoldenberg and Call Her Daddy host Alexandra Cooper were on hand to announce the launch of ‘open call’ – a new feature powered by YouTube BrandConnect, which enables brands to discover and partner with creators.
In a blog post, YouTube notes that “Open call gives creators of all sizes the opportunity to pursue new relationships with brands. And brands can lean on the relevance and trust of YouTube creators to get more from their social strategy on YouTube.”
Amelia and Alex put it more bluntly: creators can “take the middlemen out” and work directly with brands.

I was left in no doubt about the popularity of creators as the audience began to swell on the Palais’ Terrace Stage Wednesday, not for the excellent daily festival lowdown from Contagious’ Alex Jenkins and Chloe Markowitz – but for the following session featuring TikTok’s Global Head of Business Marketing and Commercial Partnerships Sofia Hernandez in conversation with creators Keith Lee and Logan Moffitt – the latter rocked to fame earlier this year with this viral cucumber salads.
It was bedlam.

Again, that sense that I was sat in a future that had already arrived.
We’re living and working in a world in which creator culture has supplanted the advertising model, in which streaming distribution has overtaken the broadcast model, in which clicks from search engines are declining as the foundations of search evolves – all of it powered by the invisible hand and accelerating force of AI (I got 650 words in without a mention, people).
In response, brands and marketers have changed their strategies and approaches to media and marketing.
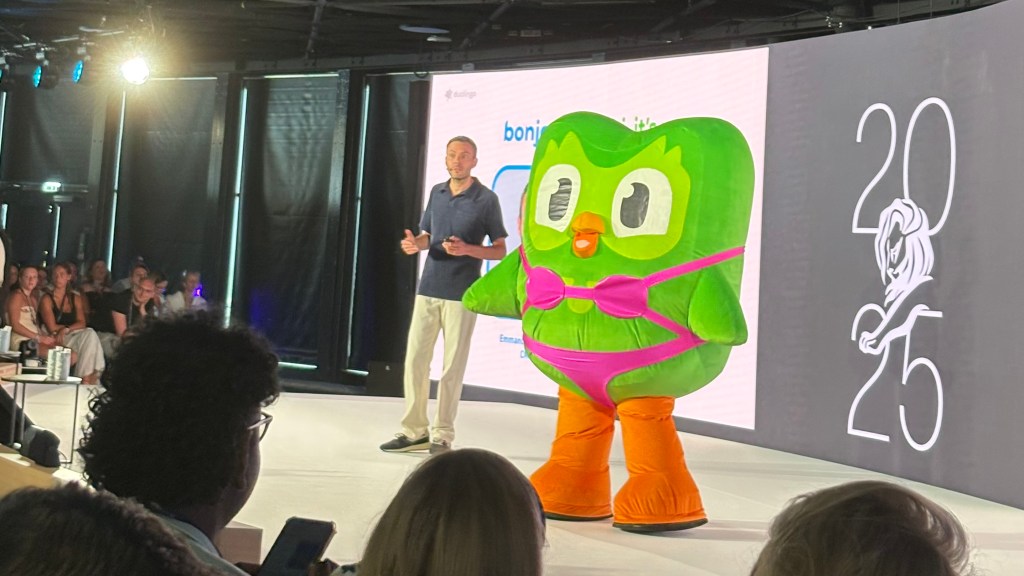
Duolingo’s Emmanuel Orssaud described how the platform eschews the conventional integrated model (too expensive, trying to do too many things, doesn’t get people talking) in favour of a social-first model where 30% of all spend is focussed not on proven effective comms but on “figuring out what else will work”. They’re expanding next into long-form content with a Duolingo Gameshow, and an anime series.

It echoes Liquid Death CEO Mike Cesario’s comments on last year’s Cannes Lions Creative Impact stage in which he shared the brand’s category-redefining approach to marketing. The brand focusses on standing out and being entertaining. The only game in town for Liquid Death is capturing attention, because “if you can get people to stop and look at your product, you’re already ahead of 99% of the market”.
Even the vibe of the awards competition this year felt like a body of work negotiating with itself. The customary smorgasbord of brands’ ideas and innovation were competing with – and often losing out to – their own past body of work.
New campaigns for Apple competed with ten years’ worth of the ‘Shot on iPhone’ campaign’, while Dove’s 2025 entries vied for metal with ‘Real Beauty for Dove’ – a 20-year-long body of work for the brand.
As Contagious’ Alex Jenkins put it – it’s a bit like bringing a gun to a knife fight.
One juror in a post-panel discussion shared with me that brand campaigns competing with the whole back-catalogue of others caused a fair bit of debate. I bet it did. The same juror indicated that they would be referring the issue to Cannes Lions. I can’t imagine it will be allowed to happen again.
So it turns out that the hero of Cannes Lions 2025 wasn’t innovation or ideas, nor was it comms platform vs tactical campaigns, or creativity vs tech or ads vs content or anything vs anything else.
The hero of Cannes 2025 was change itself.
Along La Croisette and in the Palais and everywhere in between was an industry grappling not with the future to come, but with a future that now lies behind us. The current source of unfair advantage is being able to marshal your resources – be they marketing, agency, creator, or anything in between – to leverage better than your competitors the world around you.
It’s tempting to suggest that it was ever thus; but we all know, deep down, that it’s never before been like this.
On stage in the Omnicom Space, Malcolm Gladwell noted that “There is a nobility in failure. [and that] the stories of failure are the most compelling stories that are not being told. The costs of trying crazy shit are not nearly as high as people think. This is exactly the moment to be trying crazy shit and failing!”
Or as Mercado Libre CMO Sean Summers puts it, “The industry is facing a tsunami. The biggest risk, is not taking a risk.”
//
I’ll be publishing more thoughts and perspectives from last week’s festival. Subscribe to catch the rest as soon as it drops.